Key Dates In Cyprus's Post-independence History
This month marks 50 years since the dramatic events of 1974 left the Mediterranean holiday island of Cyprus divided to this day.
On July 15, 1974, the military junta then in power in Athens engineered a coup in Cyprus seeking to end its independence and unite the island with Greece.
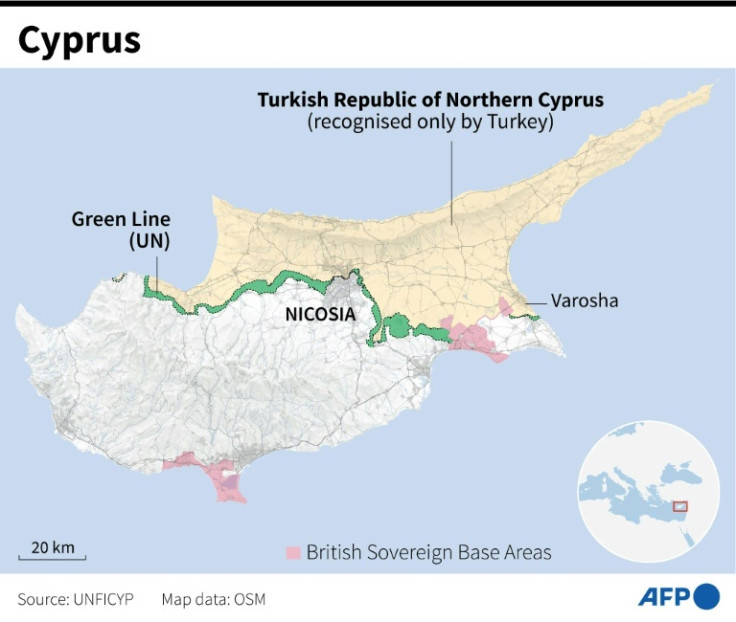
Five days later, Turkish troops landed on the north coast, beginning an invasion that saw them occupy a third of the island, including Turkish Cypriot neighborhoods of the divided capital Nicosia.
AFP looks at key dates in the island's history:
On August 16, 1960, Cyprus becomes independent from Britain after a guerrilla campaign waged by fighters aiming to unite the island with Greece.
Its constitution guarantees representation for the Turkish Cypriots, who at the time make up around 18 percent of the population, and forbids both union with Greece or Turkey and partition.
In December 1963, violence erupts between the two communities as Greek Cypriot leaders seek to override parts of the constitution. Turkish Cypriots withdraw to enclaves, some of them defended by armed fighters.
In March 1964, a UN peacekeeping force for Cyprus (UNFICYP) is established.
Between 1963 and 1974, around 2,000 people are listed as missing in clashes between the two communities.
On July 15, 1974, members of the Greek Cypriot National Guard overthrow president Archbishop Makarios in a coup sponsored by the military junta then ruling Greece.
On July 20, Turkey, invoking a 1959 agreement with Greece and Cyprus's then colonial ruler Britain, invades the north of the island saying its aim is to protect the Turkish Cypriot minority.
Three days later, the collapse of the juntas in both Athens and Nicosia leads to an interim administration and the eventual restoration of Makarios.
On July 30, Turkey, Greece and Britain meet in Geneva and establish a 180-kilometre (112 mile) long Green Line patrolled by UN troops dividing the island.
The Greek Cypriot community says the conflict left 3,000 dead and 1,400 missing. It also led to major population movements affecting around 162,000 Greek Cypriots and 48,000 Turkish Cypriots, according to the Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO).
On November 15, 1983, Turkish Cypriot leader Rauf Denktas proclaims a breakaway Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus in the 38 percent of the island controlled by Turkish troops. It is recognized only by Turkey.
In April 2003, as peace talks falter, Turkish Cypriot authorities allow Greek Cypriots to visit the north and Turkish Cypriots to travel in the other direction across the Green Line for the first time.
On April 24, 2004, Greek Cypriot voters overwhelmingly reject a UN reunification plan approved by Turkish Cypriots in a simultaneous referendum.
On May 1, Cyprus joins the European Union still a divided island, with Turkish Cypriots denied the full benefits of membership.
On September 3, 2008, the leaders of the two communities enter intensive UN-sponsored peace talks, which are joined by the three treaty powers Britain, Greece and Turkey before collapsing in 2017.
In October 2020, Turkish Cypriots elect nationalist Ersin Tatar, an ally of Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan, as their leader.
Tatar narrowly defeats pro-reunification incumbent Mustafa Akinci, in what is widely seen as a symptom of growing Turkish Cypriot disillusion over the prospects for a deal.

© Copyright AFP 2025. All rights reserved.





















